
Best adjuvant (assist) for chemotherapy | 1+1>487% |
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect, treatment, immunity.
Reduce side effects and recurrence.
Overview / Relation / Abstract / Role / Principle / Action / Mechanism / Function / Work |
What are the options for reducing cancer risks associated with HDGC?
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
Are cancer cells aggressive?
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work)
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
Solamargine vs cancer
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant. (1+1>478%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and cure.
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Extract : https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/
What are the options for reducing cancer risks associated with HDGC?
Given the increased risk of cancers associated with germline mutations in CDH1, it is recommended that people found to have this genetic mutation (called carriers) discuss the most appropriate strategies to reduce cancer risks with their health care team:
Stomach cancer: Endoscopic tests are when a thin, lighted tube is guided through the body’s gastrointestinal system to look for cancer. Although a baseline upper endoscopy exam (esophagogastroduodenoscopy or EGD) is recommended for carriers, previous studies have shown that screening endoscopy exams often miss early-stage diffuse gastric cancers.
Therefore, since endoscopic surveillance can be ineffective for preventing or detecting early-stage diffuse gastric cancers, individuals with a germline CDH1 mutation should consider having their stomach surgically removed, also known as prophylactic total gastrectomy, even if their endoscopy is normal. This type of surgery is the only proven effective way to prevent diffuse gastric cancer in individuals with HDGC. However, it is important to know that surgical removal of the stomach results in permanent changes to the digestive tract and can be associated with long-term side effects. It is very important for each patient to talk with their doctor about what tests and procedures would be appropriate for their individual care.
People who decide not to have surgery to remove the stomach may consider an intensive surveillance schedule with their doctor, with an annual EGD with multiple (more than 30) mucosal biopsies. Both the surgical and endoscopic management of people with known or suspected HDGC are best performed in centers with expertise in care of people with this syndrome.
Additional screening for women: Women at risk for HDGC are at high risk for lobular breast cancer and should talk with their doctor about breast cancer screening options at the age of 30, or 10 years before the age of the youngest breast cancer diagnosis in the family. It is not yet clear what the best breast cancer screening strategy is for women with a CDH1 mutation. Screening options include:
Monthly breast self-examinations
Clinical breast examinations performed by a doctor or nurse every 6 months
Regular breast imaging with mammograms, ultrasound, and/or a breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Since lobular breast cancer can be difficult to detect with a mammogram, breast MRI is recommended for breast cancer screening for women with a CDH1 mutation. Surgical removal of the breasts, called prophylactic mastectomy, is sometimes recommended to reduce a woman’s risk of breast cancer. Women should discuss options for reducing their breast cancer risk with their doctors.
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.
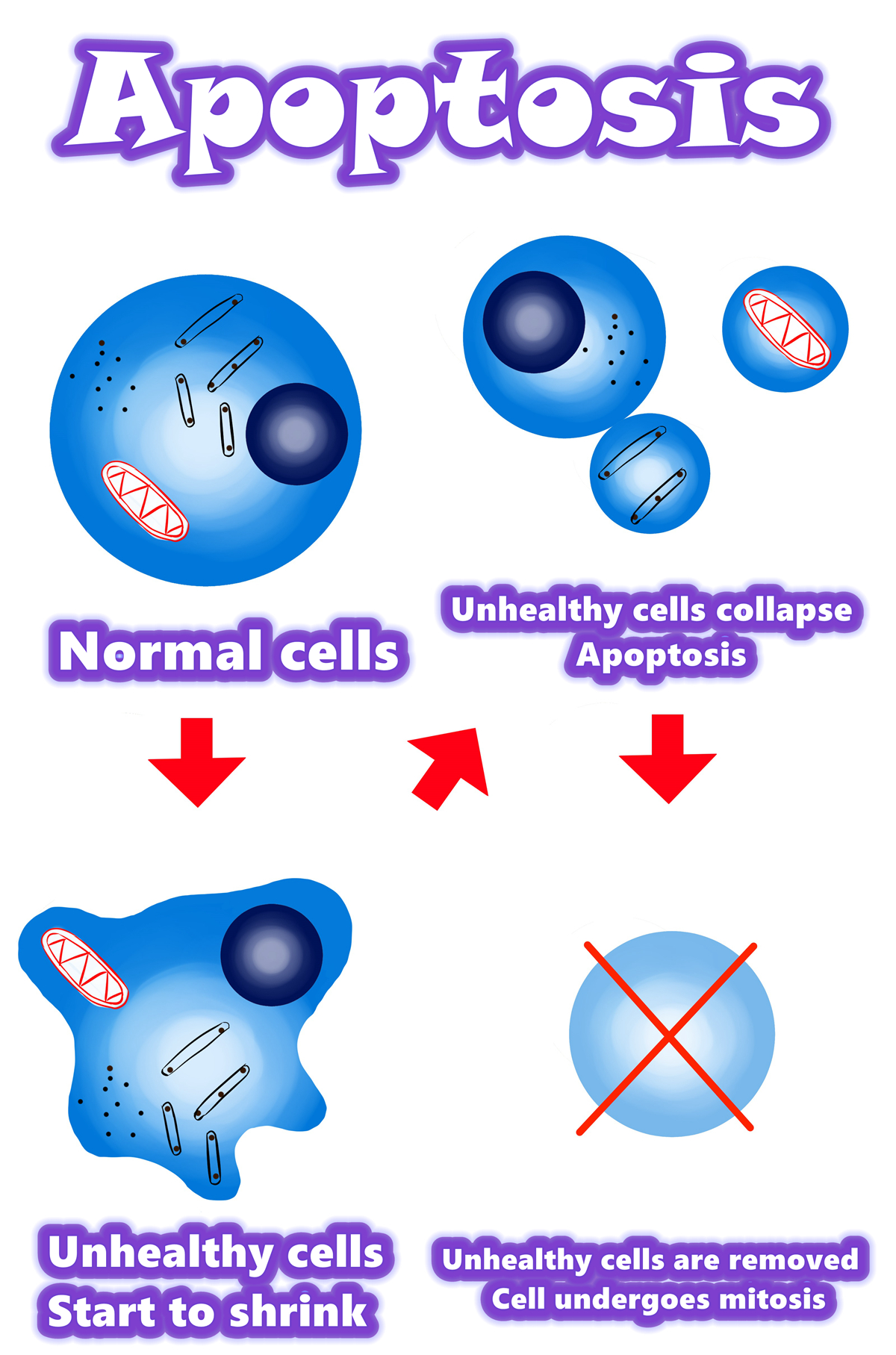
Overview of apoptosis
•Programmed cell death
•Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death, or “cellular suicide.”
•Apoptosis is different from necrosis, in which cells die due to injury.
•Apoptosis removes cells during development, eliminates potentially cancerous and virus-infected cells, and maintains balance in the body.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
- Basically, apoptosis is a general and convenient way to remove cells that should no longer be part of the organism.
- Some cells are abnormal and could hurt the rest of the organism if they survive, such as cells with viral infections or DNA damage.
- Apoptosis is part of development
- In many organisms, programmed cell death is a normal part of development.
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis
Apoptosis can eliminate infected or cancerous cells.
When a cell’s DNA is damaged, it will typically detect the damage and try to repair it.
If the damage is beyond repair, the cell will normally send itself into apoptosis, ensuring that it will not pass on its damaged DNA.
When cells have DNA damage but fail to undergo apoptosis, they may be on the road to cancer.
However, “successful” cancer cells successfully evade the process of apoptosis.
This allows them to divide out of control and accumulate mutations (changes in their DNA).
Apoptosis is key to immune function
Apoptosis also plays an essential role in the development and maintenance of a healthy immune system.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
The symptoms of cancer cells are in the nucleus.
The nucleus controls the outer cytoplasm, cell composition, cell viability, etc.
DNA mutations also mutate in the nucleus.
Therefore, to treat cancer cells, we must first enter the nucleus.
Let the “regulatory cell gene” mechanism enter the nucleus to regulate
Are cancer cells aggressive?
After the action of Solamargine, the aggressiveness of cancer cells is alleviated.
So after using Solamargine, many patients feel that I am half better.
Although the tumor does not disappear quickly, patients feel that the degree of aggressiveness is reduced.
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work).
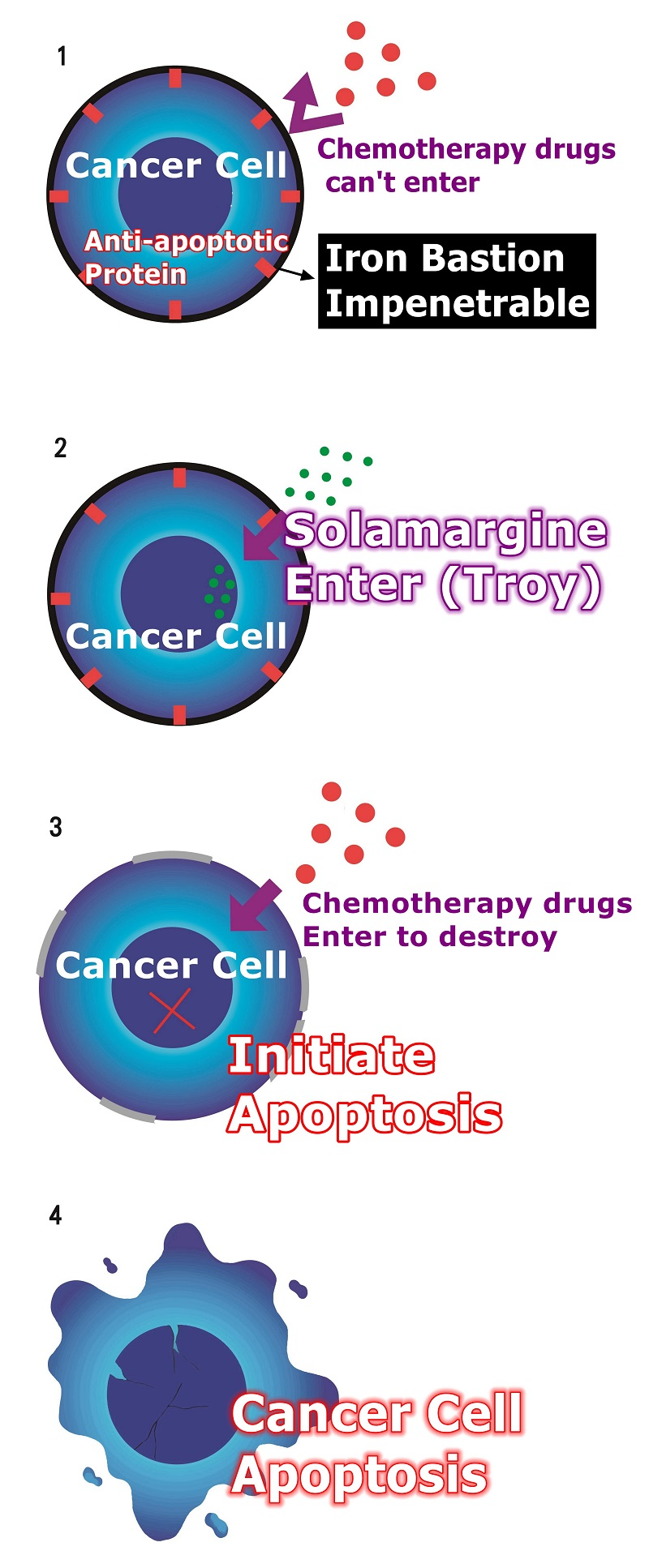
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
When Solamargine enter,
Solamargine activates receptors that are turned off by cancer cells, allowing cancer cells to modulate again.
Solamargine modulates the anti-modulates genes of cancer cells, making cancer cells less resistant.
Reduced drug resistance
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Solamargine modulates the mutated genes in cancer cells and then initiates cancer cell apoptosis to achieve anti-cancer effects.
Solamargine combined with which chemotherapy drugs are more effective in treating cancer cells?
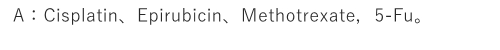
Solamargine vs cancer
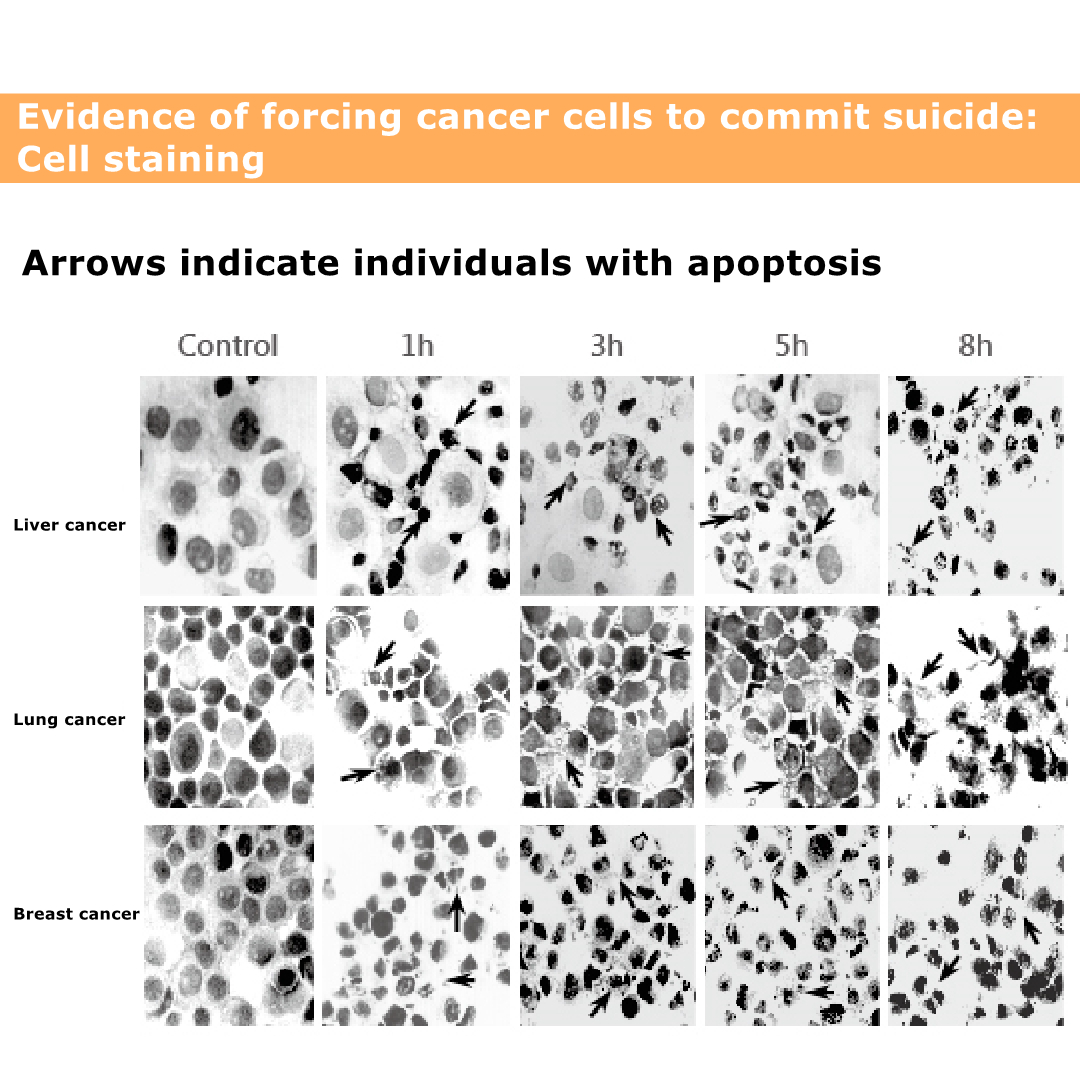
Solamargine vs cancer
The picture shows the death of cancer cells.
The black and black parts are cancer cell nuclei.
Even if the nucleus ruptures, the cancer cells will die.
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
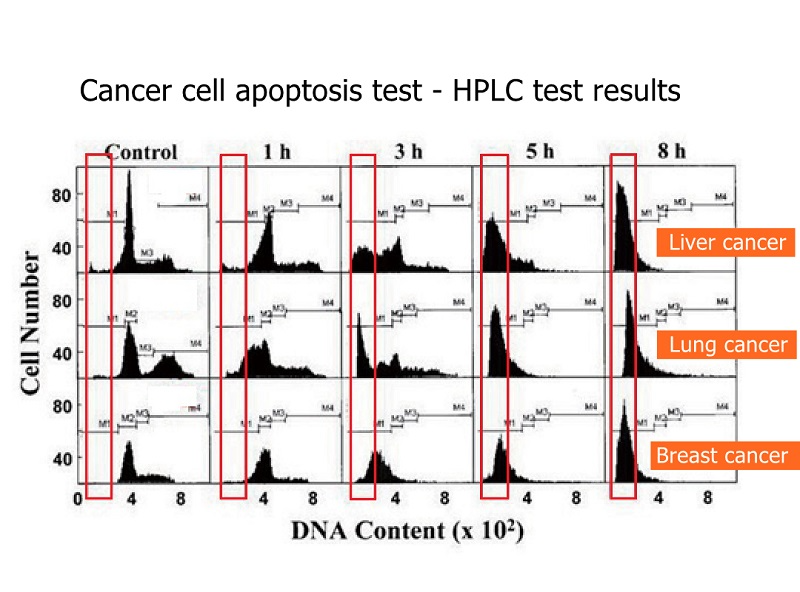
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
The figure shows that the death of lung cancer cells is relatively slow, and it will not be obvious until eight hours later.
The figure shows that the death of liver cancer cells is very obvious, even more obvious in eight hours.
The graph shows that breast cancer cells die faster. It was obvious from the beginning that breast cancer is easy to treat, and patients with breast cancer need not worry.
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant. (1+1>487%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and treatment.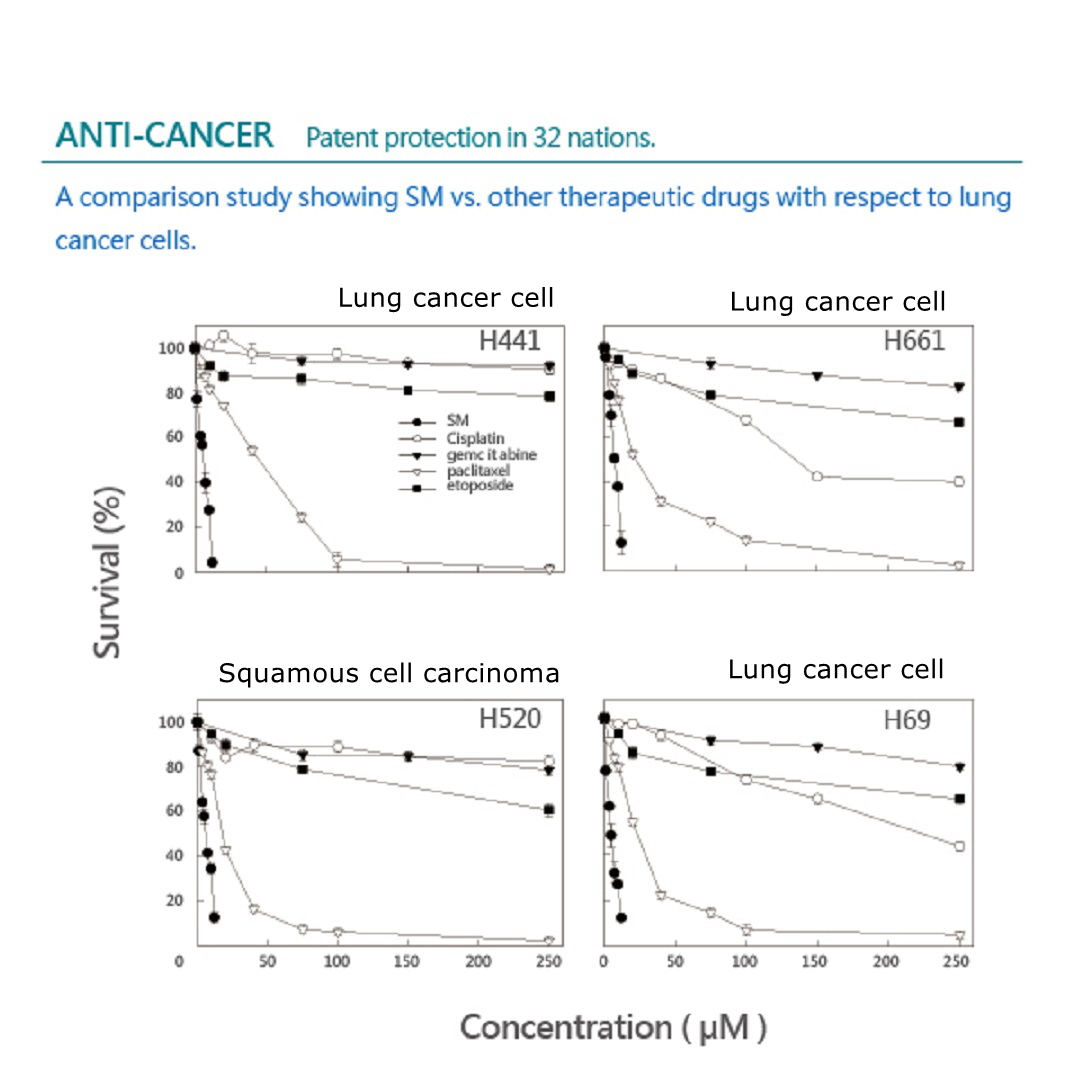
ANTI-CANCER
Patent protection in 32 nations.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other therapeutic drugs with respect to lung cancer cells.
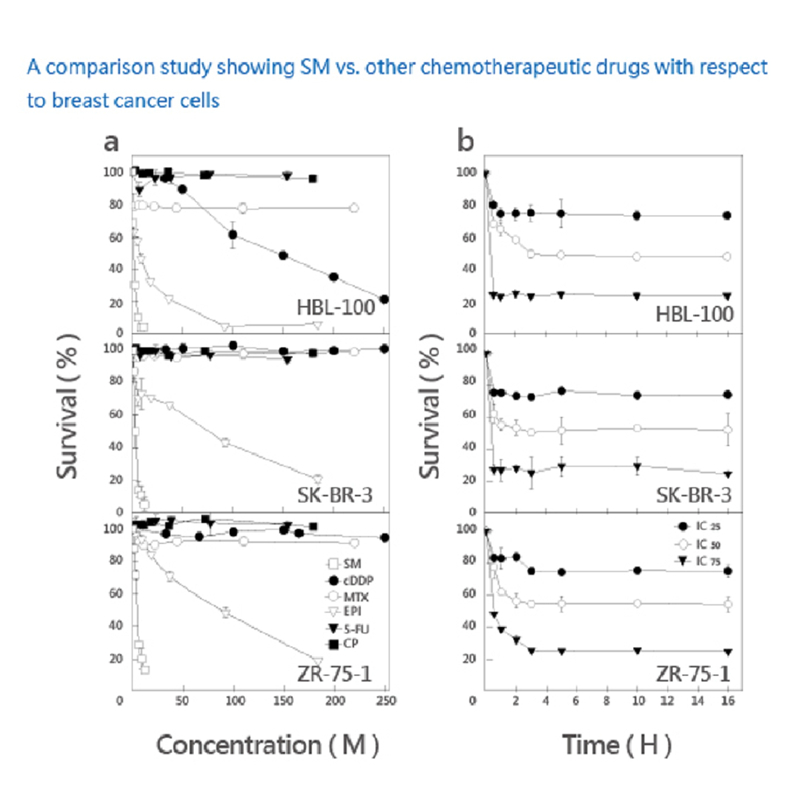 A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
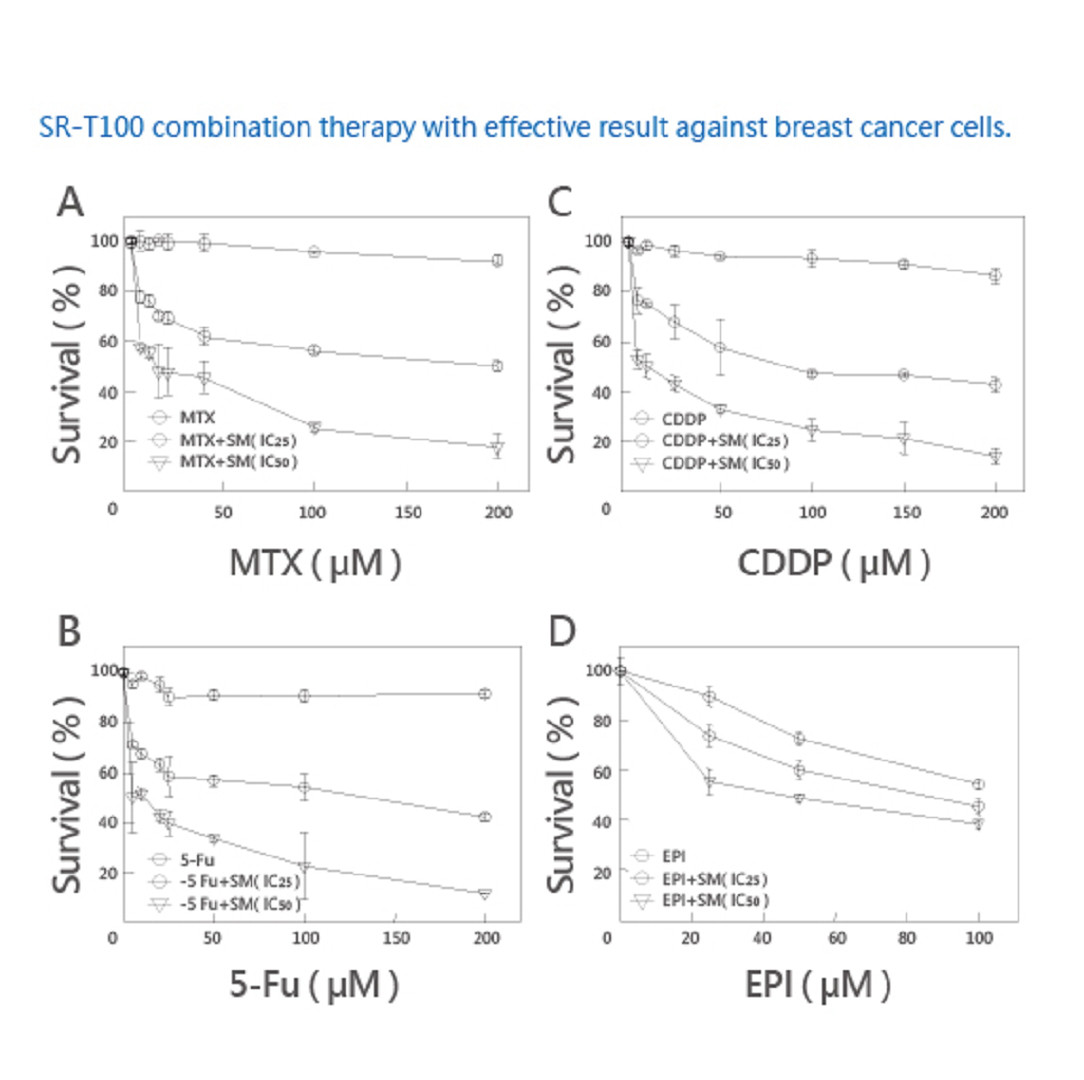
SR-T100 combination therapy with effective result against breast cancer cells.
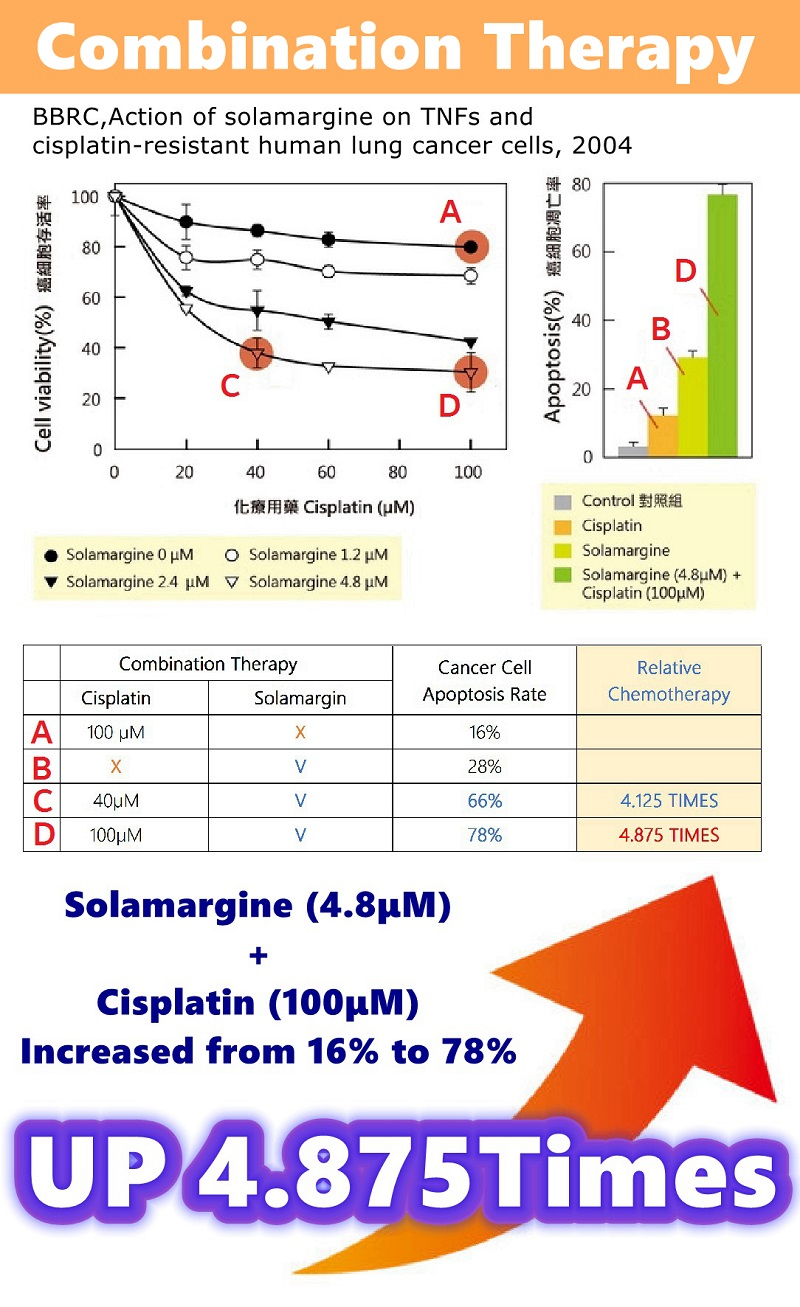
Combination Therapy | Research results for lung cancer cells.
A. Chemotherapy (100μM), 16% of cancer cell apoptosis.
B. Alone SM (4.8μM), 28% of cancer cell apoptosis.
C. SM (4.80μM) + Chemotherapy (40μM), 66% of cancer cells apoptosis.
D. SM (4.80μM) + Chemotherapy (100μM), 78% of cancer cell apoptosis.
SM has a clearing effect better than Chemotherapy.
The combined treatment of Solamargine and Chemotherapy significantly increased the apoptosis of lung cancer cells.
SM (4.8μM) + Chemotherapy (40μM), increased from 16% to 66% (up to 4.125 times).
SM (4.8μM) + Chemotherapy (100μM), increased from 16% to 78% (up to 4.875 times).
Reorganized from: BBRC. Action of Solamargine on TNFs and drug-resistant human lung cancer cells 2004.
The best solution for cancer cells.
